.
Digital Image Basics for non-Photographers • Blaise Tobia
.
.
Image Mode
The default color image mode - and the only color mode that can be saved in a JPEG file - is RGB.
RGB file information is contained in three separate channels, one dedicated to Red color information, one to Green and one to Blue.
Each channel is like a separate partial-color image in registration with the other two partial-color images.
When all three channels are visible, a composite, RGB image is displayed.

Recording and displaying color images using R, G and B separations was first demonstrated by physicist James Clerk Maxwell in 1861.
Almost a century later, this additive primaries color system became the basis for the color television,
which used an RGB picture tube; it was later adapted to serve color computer monitors.
Current LCD color monitors and projectors also use an RGB imaging system.
B+W photographic images can be viewed and saved in grayscale mode, with just just one channel.
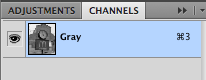
Note, however, that when a grayscale image is displayed on an RGB device
such as an LCD computer monitor,
all three color elements are active, but are balanced for apparent color neutrality.
Accordingly, B&W images are now generally saved as RGB JPEG files.
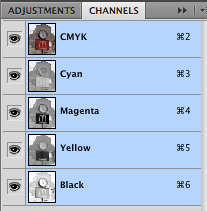
For special purposes (usually related to color printing) color images may be viewed and saved in CMYK mode.
Cyan, Magenta and Yellow are the subtractive color primaries.
With the addition of extra blacK, they can be used for color offset printing.
(Inkjet printers also use CMYK - but generally are designed to receive RGB files that they will then convert.)
.
.
Color resolution (or depth)
"Full Color" is used on this website to mean 8-bit per channel color.
An 8-bit color channel distinguishes 256 levels
of that color.
If an image is in 8-bits/channel mode, and there are 3 channels (RGB) then there is a total of 24 bits of color information.
This means 256x256x256 =
16.7 million distinct colors (at least in theory).
"Indexed Color" means a more limited palette of just 256 distinct colors. It is the color depth of the GIF file format.
This mode is better suited to graphics than to photographs, since color subtlety can be lost and, sometimes, banding can occur.
 ....
....
The left-hand version is full color (24-bit); the right version is indexed color and shows banding in the blue area.
Standard JPEG image files are RGB-8 (8 bits per channel); many times this will be stated simply as "RGB" since
the extra-depth color modes RGB-16 and RGB-32 cannot be saved in JPEG format.
.
Color Space
Color Space is often confused with Color Profile (even within Photoshop)

Adobe RGB is a color space, as is sRGB, not a color profile.
.A color space is a limitation on the range of colors specified in a digital image file.
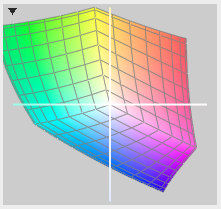
Adobe RGB (on the left, below) encompasses a larger range of colors - necessary for high quality photo printing.
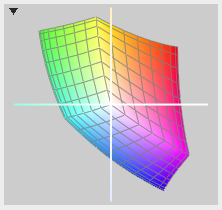
sRGB (on the right, below) encompasses a smaller range of colors - but is optimized for on screen presentation.
(You should see on your screen that the corners of the sRGB graph seem more saturated.)
 ....
....
A color profile is a formula for color-correction of any real-world (and hence imperfect) color device.
There are profiles for getting good, neutral, colors from digital cameras, scanners, monitors, printers.
A color profile is not part of a digital image (unlike a color space) - it translates an image to a device or vice-versa.
Most browsers and image viewers, as well as image-embedding programs, now preserve and recognize color space information,
so it is a good habit to be sure that your image files have a designated color space and that you use color space consistently.
You should also be sure to have a good, neutral color profile controlling your color monitor (or laptop screen)
so that you know your images will be seen in the intended color by those who will view them
(assuming that they also have well profiled monitors or projectors!) .